计数排序是桶排序思想的一种,适合以下场景:
- 数值范围小,但数量大,例如给1w个学生的考试成绩进行排序
流程比较简单:用一个计数数组记录每一个数字出现的次数,然后遍历计数数组,按顺序一一填充到新数组中。
举个最简单的例子:
原数组:
[0,2,1,2,2,3]遍历原数组,出现一个0,则
countArray[0]++, 出现一个3,则countArray[3]++,出现一个n,则countArray[n]++原数组中,0出现1次,1出现1次,2出现3次,3出现1次。最终计数数组记为:

值得注意的是,数组下标和原数组的数值是对应的,例如2出现了3次,则array[2] = 3
然后填到新数组中:
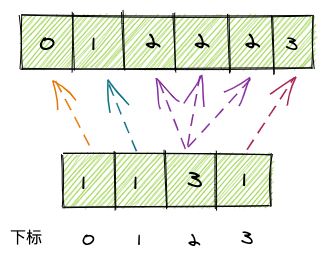
不过以上方法有个问题:如果原数组中最小的值不是0,比如是100,那么计数数组下标0~99的空间就浪费了,例如给[100,101,103,102]排序:
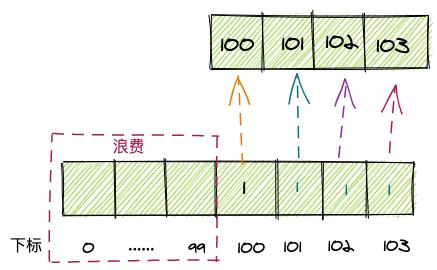
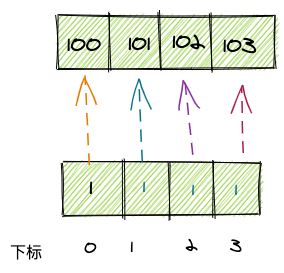
因此我们需要做一个小小的改动。
100出现的数量原本应该记录在下标100的位置,现在改为记录在下标100-100=0的位置上,103出现次数记录在下标103-100=3的位置上:
代码示例:
public class Count {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = { 9, 8, 2, 2, 3, 8, 1, 4, 5, 6, 3, 5, 2};
int[] result = countSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result));
}
private static int[] countSort(int[] array) {
int[] result = new int[array.length];
// 找到数组中最大值和最小值
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
max = Math.max(array[i], max);
min = Math.min(array[i], min);
}
int[] countArray = new int[max - min +1];
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
countArray[array[i] - min]++;
}
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < countArray.length; i++) {
while (countArray[i] > 0) {
result[j] = i + min;
j++;
countArray[i]--;
}
}
return result;
}
}进阶版
如果有一个需求,根据学生成绩排序,如果成绩相同的,按照原数组的顺序排序
例如有以下数据需要排序
| 学生A | 学生B | 学生C | 学生D | 学生E |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 | 97 | 94 | 94 | 96 |
预期排序后结果为:
| 学生A | 学生C | 学生D | 学生E | 学生B |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 | 94 | 94 | 96 | 97 |
如何用计数排序实现呢?这个问题稍微有点复杂,首先我们先列出这个[90,97,94,94,96]的计数数组:
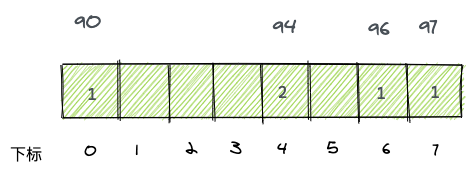
现在我们要改造这个计数数组,每一个元素的值都加上前面所有元素值的和。例如
array[4] = array[4] + array[0]array[6] = array[6] + array[4] + array[0]array[7] = array[7] + array[6] + array[4] + array[0]
经过改造前后,计数数组如下:
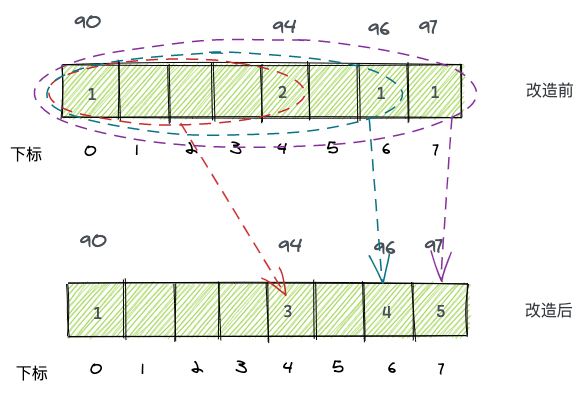
为什么要这么做呢?
以array[6] = array[6] + array[4] + array[0]为例
array[0]代表的是原数组元素0(实际是90)出现的次数,array[4]代表4出现的次数,相加就是0和4出现的次数的总和。
回忆下计数排序最后一步“回填到新数组”的过程,这两个相加其实就是新数组中6(实际是96)的数组下标,换句话说就是6的排名。
改造计数数组之后,回填的方式也要需要有所改变,不再是直接遍历计数数组,而是要从后往前遍历原数组。
以上面的数组为例,原数组和计数数组为:
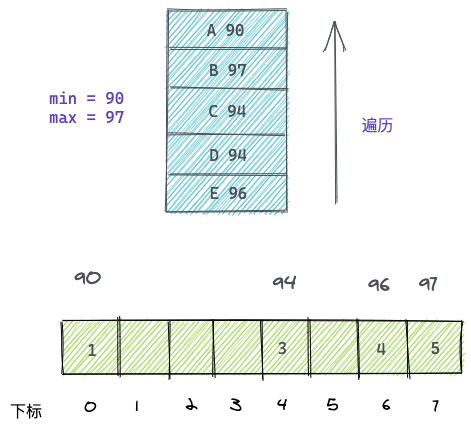
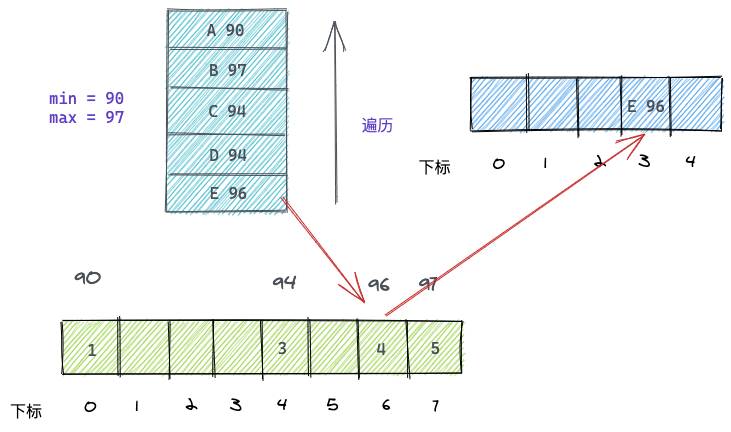
遍历第一个学生E-96,在计数数组中找到countArray[96-90], 值是4,说明E学生排名第4,则填入结果数组下标为3的位置(排名减一才是数组下标)。
且countArray[96-90]--,表示之后遍历如果遇到分数为96的同学,那么他的排名就是3
如下图:
同理,将D和C同学也进行相同处理,D和C分数一样,排序和原数组一致:
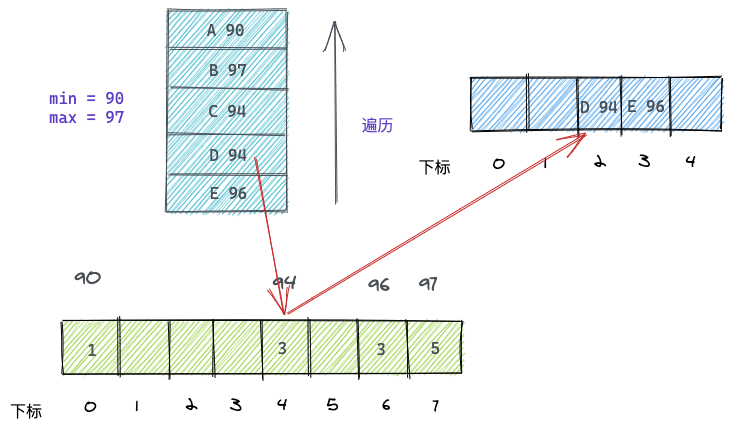
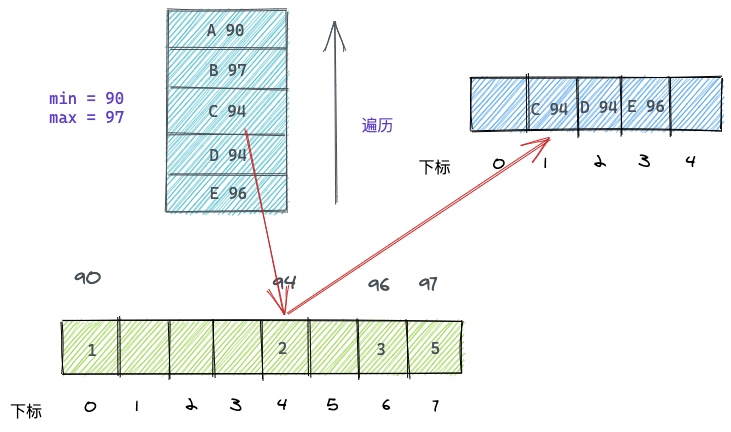
其他元素以此类推。
进阶版代码示例:
public class Count2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student[] students = new Student[]{
new Student("A", 90),
new Student("B", 97),
new Student("C", 94),
new Student("D", 94),
new Student("E", 96),
};
Student[] sortedStudents = countSort(students);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sortedStudents));
}
private static Student[] countSort(Student[] array) {
// 找到数组中最大值和最小值
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
max = Math.max(array[i].getSocre(), max);
min = Math.min(array[i].getSocre(), min);
}
int[] countArray = new int[max - min + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
countArray[array[i].getSocre() - min]++;
}
// 给统计数组做变形
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < countArray.length; i++) {
if (countArray[i] > 0) {
sum += countArray[i];
countArray[i] = sum;
}
}
Student[] result = new Student[array.length];
// 从后往前遍历原数组
for (int i = array.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
int index = array[i].getSocre() - min;
int resultIndex = countArray[index] - 1;
result[resultIndex] = array[i];
countArray[index]--;
}
return result;
}
private static class Student {
private String name;
private int socre;
private Student(String name, int socre) {
this.name = name;
this.socre = socre;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getSocre() {
return socre;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", socre=" + socre +
'}';
}
}
}
